Break From the Language Learning Plateau As Intermediate Learners
Read other articles:
Back to posts
Table of Contents

If you’ve ever felt stuck in your language-learning journey—where progress seems painfully slow despite your efforts—you’re not alone. This frustrating stage, often called the language learning plateau, is common among intermediate learners. But understanding why it happens and how to address it can help you break through and reignite your progress.
In this blog, we’ll explore the causes of the language learning plateau, why it happens, and practical strategies—rooted in Stephen Krashen’s theories and proven techniques—to help you push past it and continue your journey to fluency.
What Is the Language Learning Plateau?
In the early stages of language learning, progress feels exhilarating. You quickly build foundational vocabulary, grasp basic grammar, and start recognizing common phrases. This rapid improvement makes the learning process feel rewarding and motivating. However, as you move into the intermediate stage, progress slows. Why?
- Initial Rapid Gains vs. Increased Complexity
Beginners often tackle “low-hanging fruit”—essential words and straightforward grammar. At the intermediate level, however, learners face subtler challenges like idiomatic expressions, nuanced grammar, and less frequent vocabulary. The result? Progress becomes less noticeable. - Diminished Perceived Gains
Intermediate learners can hold basic conversations and understand everyday texts, but achieving fluency requires mastering complexities like native-like comprehension, colloquialisms, and advanced syntax. These goals take longer, making it feel like you’re stuck in a language-learning plateau. - Emotional Impact
Frustration from slower progress can dampen motivation, creating a cycle where learners avoid challenging themselves, further reinforcing the plateau.
Krashen’s Theories and the Plateau Effect

Renowned linguist Stephen Krashen provides valuable insights into why the language learning plateau happens and how to overcome it. Here’s how his key hypotheses apply:
1. Comprehensible Input Hypothesis
Krashen emphasizes the importance of input at the i+1 level—content slightly above your current proficiency.
- Plateau Cause: Intermediate learners often consume material that’s either too easy (i+0) or too difficult (i+2), leading to stagnation.
- Solution: Seek content tailored to your level, like graded readers, podcasts, or TV shows designed for language learners. For example, subtitles in the target language can bridge the gap between understanding and challenge.
2. Affective Filter Hypothesis
Emotional factors like frustration or anxiety can block language acquisition.
- Plateau Cause: Feeling stuck or inadequate raises the affective filter, making learning more stressful and less effective.
- Solution: Lower your affective filter by focusing on enjoyable, low-pressure activities—watching fun shows, engaging in casual conversations, or reading for pleasure. The more relaxed and motivated you feel, the better you’ll learn.
3. Natural Order Hypothesis
Krashen posits that language structures are acquired naturally, and some take longer to master.
- Plateau Cause: Intermediate learners often struggle with complex structures (e.g., conditionals, idioms) that naturally require more time to internalize.
- Solution: Be patient and focus on exposure rather than forcing mastery. These structures will come with consistent input and practice.
4. Input vs. Output
Krashen argues that input drives output—speaking and writing emerge naturally after sufficient exposure.
- Plateau Cause: Learners may push too hard to produce perfect speech without prioritizing input, leading to frustration.
- Solution: Focus on rich, engaging input like podcasts or books. Shadowing techniques (repeating speech in real-time) can bridge the gap between input and output.
Practical Strategies to Break Through the Language Learning Plateau

Here are actionable tips to reignite progress and overcome the plateau:
1. Diversify Your Input
Seek materials aligned with the i+1 principle:
- Podcasts and Videos: Choose content slightly above your level. Use subtitles in your target language to enhance comprehension.
- Reading Material: Explore news articles, blogs, or simplified novels that challenge you without overwhelming.
2. Shadowing and Active Listening
Shadowing—repeating after native speakers—combines listening and speaking, improving pronunciation and fluency. Active listening, where you focus on details like intonation and word usage, also reinforces language patterns.
3. Reevaluate Your Goals
At this stage, shift your goals from quantity to quality. Instead of aiming for broad fluency, set specific objectives:
- Read one book in your target language.
- Hold a 10-minute conversation with a native speaker.
Breaking larger goals into smaller, measurable ones boosts motivation and tracks progress.
4. Interaction Without Perfection
Perfectionism can stall progress. Instead, join language exchange groups or online forums where mistakes are welcomed as part of learning. Platforms like Reddit’s language communities or conversational apps provide supportive spaces to practice.
5. Focus on Enjoyment
Engage with content that genuinely interests you. Motivation is a powerful driver, and finding joy in the process keeps the affective filter low. Whether it’s a gripping TV series, cooking tutorials, or travel blogs, make learning fun.
A Tool to Help You Push Through
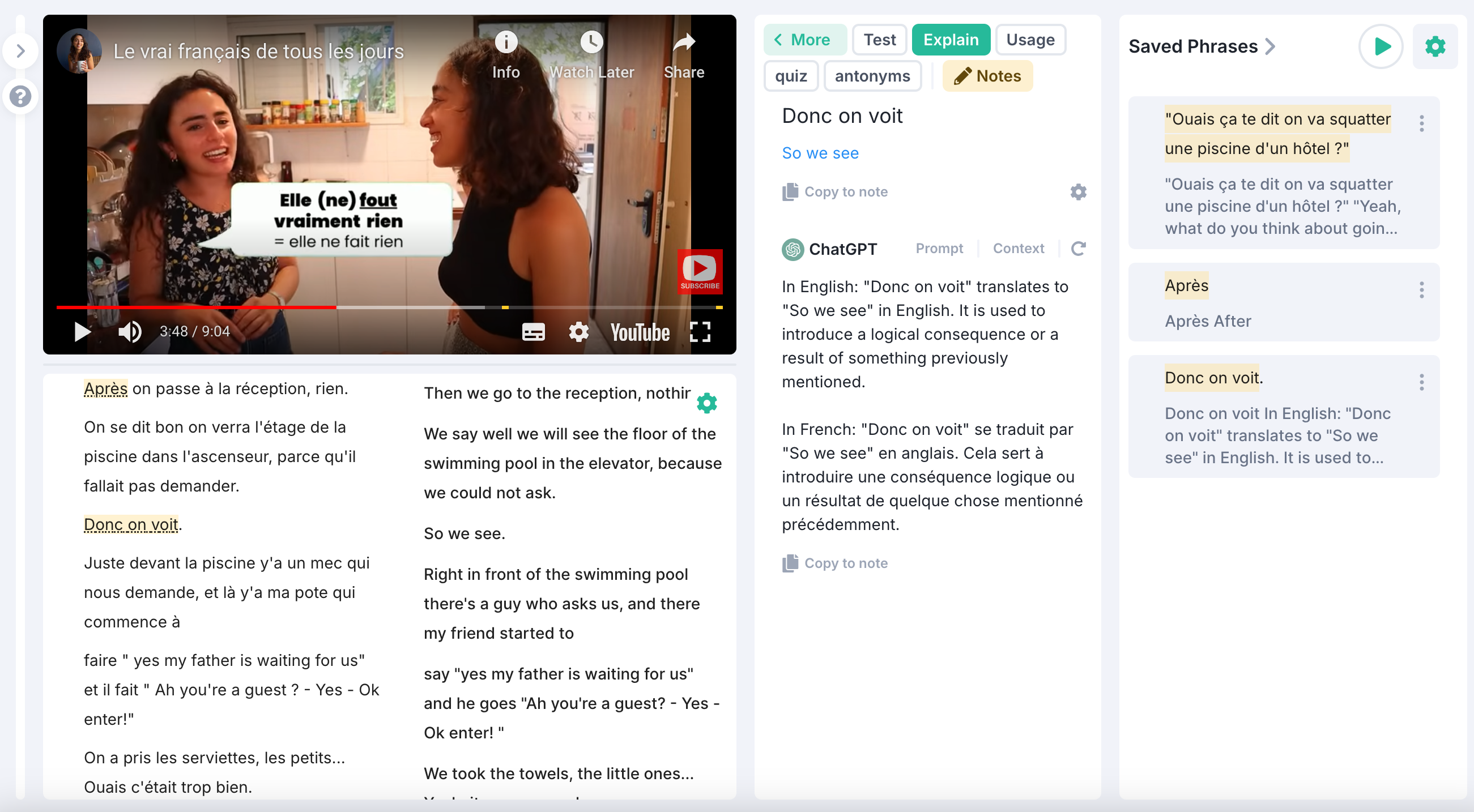
If you’re looking for a resource that embodies Krashen’s principles, LangMagic offers tailored solutions for breaking through the language learning plateau. By combining comprehensible input with tools like interactive transcripts, contextual vocabulary, and shadowing exercises, LangMagic ensures you’re constantly exposed to i+1 content.
One standout feature is its audio-podcast tool, perfect for revisiting class content and vocabulary in context. Whether you’re commuting, walking, or relaxing, it keeps your learning consistent and engaging. LangMagic bridges the gap between input and output, helping you build confidence and fluency naturally.
Our Final Thoughts
The language learning plateau is a normal part of language learning, signaling a shift to more advanced skills. While it can feel discouraging, understanding its causes and applying strategies rooted in Krashen’s theories can help you move forward. Focus on consistent exposure, enjoy the process, and trust that progress—though slower—continues to happen.
Remember, language learning is a journey, not a race. With the right mindset, tools, and techniques, you can overcome the plateau and achieve the fluency you’re aiming for. Keep going—you’ve got this!
Read other articles:
Back to posts
